- What is a Patent in India?
A patent is an Intellectual Property Rights with respect to inventions. It is a grant of exclusive right provided by the Government of India for a limited period in exchange of full disclosure of the invention.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is a provisional patent application in India?
Under Section 9 of Indian Patent Act 1970, there exist two types of patent specifications, that is, Provisional Patent Specifications and Complete Specification. It is a preliminary application before filing a usual patent. When the invention is at the stage of research and development, then the description of the invention can be made as per provisional patent application and submitted to the patent office in order to secure the priority date of the invention.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What are the ways of Filing Patent Application with Indian Patent Office (IPO)?
As per the Indian Patents Act, an inventor, his assignee or legal representative, who before his death was either the inventor or assignee, can apply for patent at the Indian Patents Office or its branches depending upon whose jurisdiction he resides or has his domicile or place of business. A patent application can be in a form of Ordinary Application which can be both Provisional Application or Non-Provisional Application. The forms can be submitted in the patent office or can be submitted online if an inventor has a Class 3 digital certificate.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Patent Novelty in India?
Novelty means ‘the newness of the information that is generally unused or unknown and that gives its owner a competitive advantage in a business field. Novelty is a part of legal test to determine whether a particular invention is patentable. The purpose is to prevent the prior art from being patented again.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Prior Art in India?
The word prior art in Indian Patent law means any information which has been made available in the public domain and related to the knowledge existing prior to the date of invention.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What are Patent Application types in India?
The different types of Patent applications are:-
- Ordinary Application
- Convention Application
- PCT International Application
- PCT National phase Application
- Application for Patent of Addition
- Divisional Application
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is PCT National Phase Patent Application in India?
The PCT is an international agreement that helps to simplify the process of filing patent applications in several countries. Within 31 months from the priority date, the application enters the National Phase PCT application. The National Phase of a PCT patent application resembles a national filing in a respective country. The filing of PCT patent application is much simpler than the filing of normal national application since most of the formal requirements are resolved in the international phase itself.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Patent Applications filing process in India?
The procedure includes:-
- Filing of the Patent Application
- Publication of Patent Application
- Examination of Patent Application
- Grant of Patent Application
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is online patent filing in India?
E – filing services for Patents was launched in the year 2007 which enabled online filing of new applications for Patents. The Indian Patent office has developed the e-filing system so as to cover comprehensive e-filing for Patents, wherein, in addition to online filing of New Applications, subsequent filings have also been integrated. It includes web based filing, Dual way login, Provision for filing of all entries as per Schedule 1 of the Patents Rules, 2003, Proper Validations with IPO Patent database, Facility to the digital signatures and Improved procedures to minimize transaction errors.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- How does online patent filing works in India?
Visit the comprehensive e-filing portal. Certain requirements before the registration to be done through online portal are: Operating System, Web Browser, Digital signatures and Payment Gateways. Fill the registration form. If a user is already registered he can log in using the User ID and Password or Digital signature. In the event of password loss, user can login with Digital Signature and reset the password.
Once logged in, the users can also file their applications using the “Quick form filing” option.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is the patent granting procedure in India?
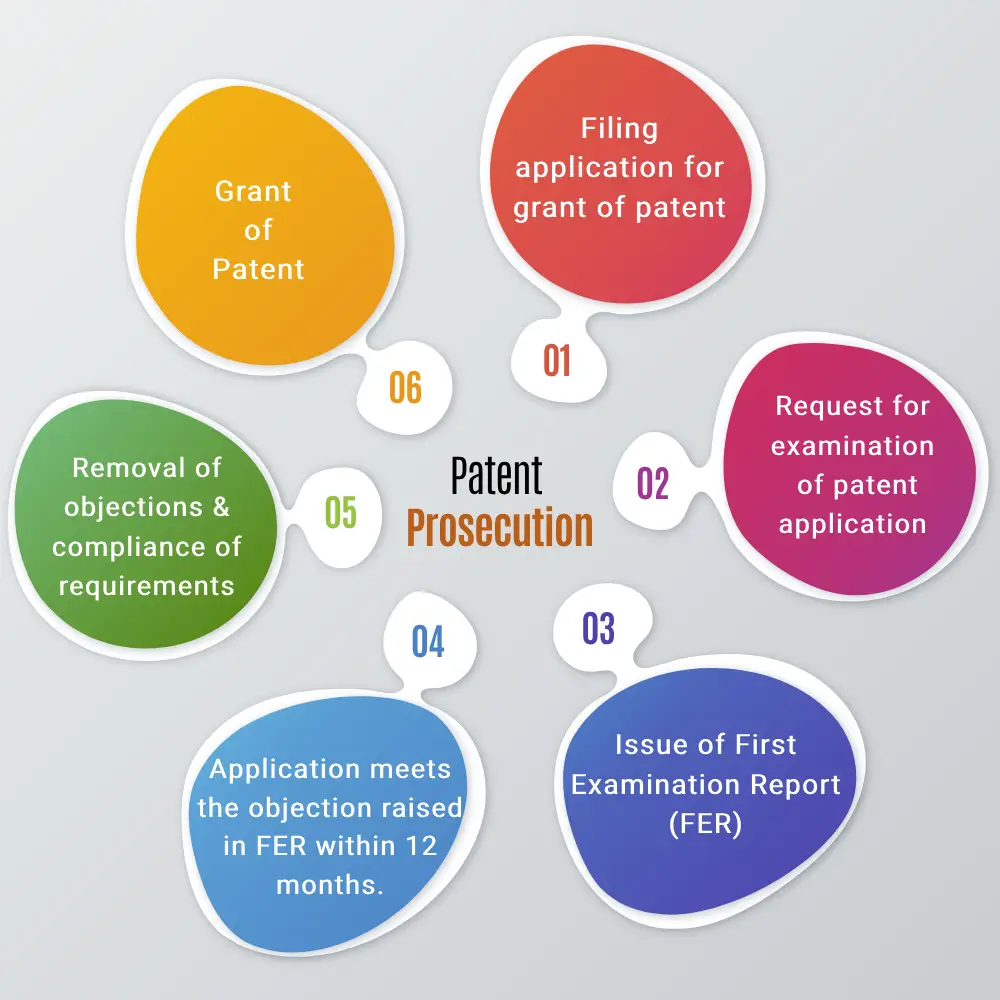
After filing the application for the grant of patent, a request for examination is required to be made for examination of the application by the Indian Patent Office. After the First Examination Report is issued, the Applicant is given an opportunity to meet the objections raised in the report. The Applicant has to comply with the requirements within 12 months from the issuance of the First Examination Report. If the requirements of the first examination report are not complied with within the prescribed period of 12 months, then the application is treated to have been abandoned by the applicant. After the removal of objections and compliance of requirements, the patent is granted and notified in the Patent Office Journal.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Publication of Patent Application in India?
As per the provisions envisaged in the Indian Patents Act, 1970, an Indian patent application can be published in two possible manners – automatic publication and early publication. A patent application automatically gets published within 18 months from the date of filing of the application. Under this provision, an applicant is not required to make any request for publication as it is a mandatory step in the process of grant of a patent. A patent application can be published early by filing a request for the same in Form 9.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Examination of Patent Application in India?
Once a patent application is filed in India and published after 18 months of filing the application, the next step involved is the examination of the patent application. The examination process starts once the applicant files a request for examination within 48 months from the date of filing of the application or the priority date whichever is earlier. During the first examination stage, the examiner prepares the examination report incorporating all the statutory objections for the given patent application. The examiner performs a patent search in order to identify the prior arts relevant to the invention.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is the term of Patent Rights in India?
Term of every patent in India is 20 years from the date of filing of patent application, irrespective of whether it is filed with provisional or complete specification. However, in case of applications filed under PCT the term of 20 years begins from International filing date.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- Can a Patent be renewed in India?
The patentee has to pay renewal fee according to Sec 53 of the Indian Patent Act. Renewal fee or Maintenance fee is paid every year for keeping a patent in force for the term of patent. Renewal fee specified in the first schedule is payable before the expiration of the second year from the date of patent in respect of third year. Thereafter, renewal fee should be paid before the commencement of every succeeding year. However, this period is extendable by six months by requesting extension of time. If the patentee fails to pay the renewal fee within the prescribed period and also within the extendable period of six months by requesting extension of time, the patent ceases to have effect or lapses from the date of expiration.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Patent revocation in India?
Under Section 64 of the Indian Patents Act, the patent revocation can be affected. It means cancellation of the rights granted to a person by the grant of a patent.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Compulsory Licensing of Patents in India?
Under Indian Patent Act, 1970, the provision with regard to compulsory licensing is specifically given under Chapter XVI.
- As per Section 84, any person who is interested or already the holder of the license under the patent can make a request to the Controller for grant of Compulsory License on patent after three years from the date of grant of that patent on the existence of conditions mentioned in the Section 84 of the Patents Act, 1970
- While granting the compulsory license, the Patent office will take into account measures such as the nature of the invention, any measures already taken by the patentees or any licensee to make full use of the invention, ability of the applicant to work the invention to the public advantage and time elapsed since the grant of the patent.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is Patent Infringement in India?
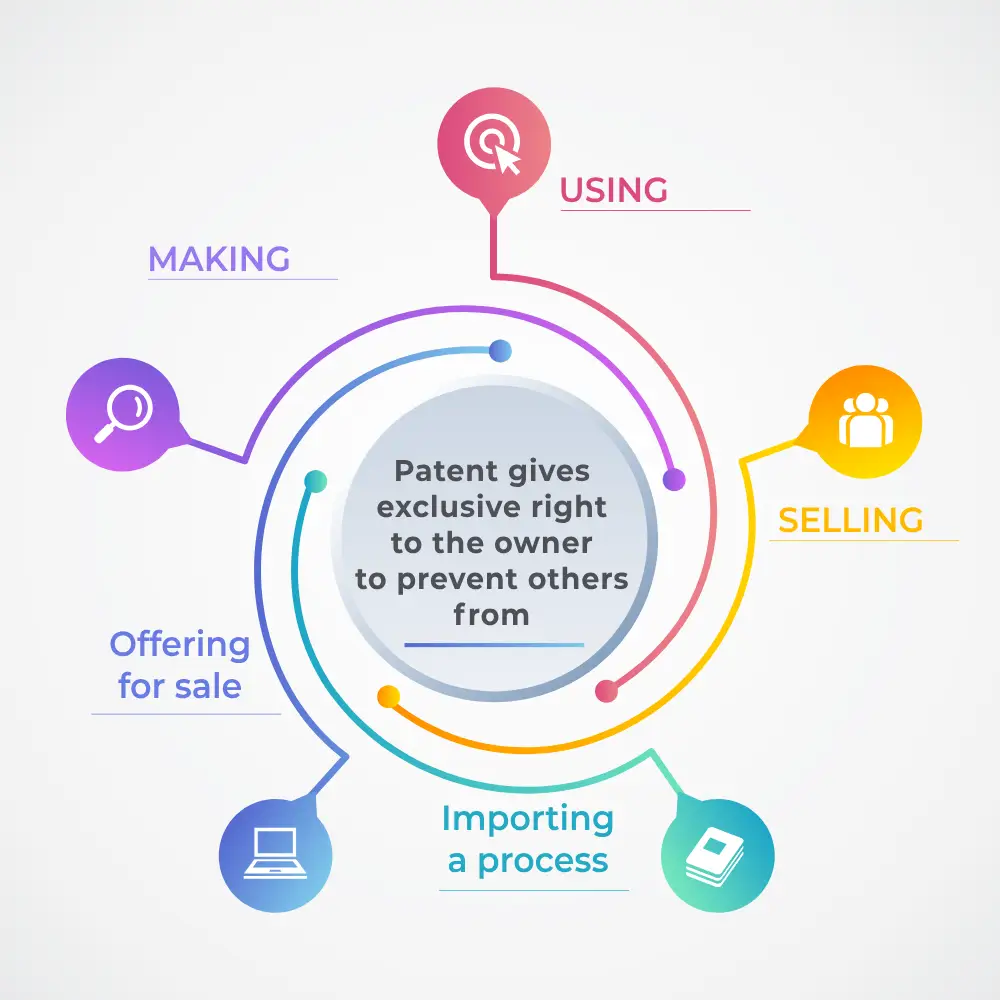
Activities that constitute Patent Infringement has not been specifically defined in India. However, Section 48 of the Indian patent Act, confers exclusive right on the patentee to exclude third parties from making, importing, using, offering for sale or selling the patented invention, patented product or patented process.
Read more at www.ssrana.in
- What is a Patent?
Patent is an exclusive statutory right granted by the State for an invention that is:

2. Why is it necessary to register an invention as Patent?
Under the World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS), patents should be available in WTO member states for any invention in all fields of technology.
3. Steps involved in grant of Patent
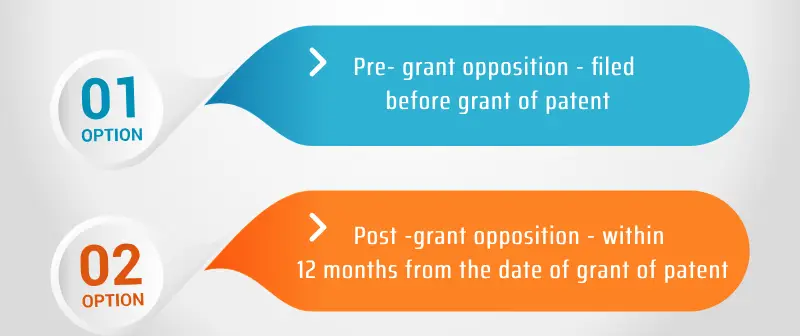
4. Can anyone oppose a Patent application?
Yes, a patent application can be opposed once it is published. There are following two types of patent opposition under the Indian Law:
5. What is the term of a patent in India?
The term of a patent is twenty years from the date of filing the patent application.
6. What are the advantages of grant of Patent?
7. What inventions are not patentable in India?
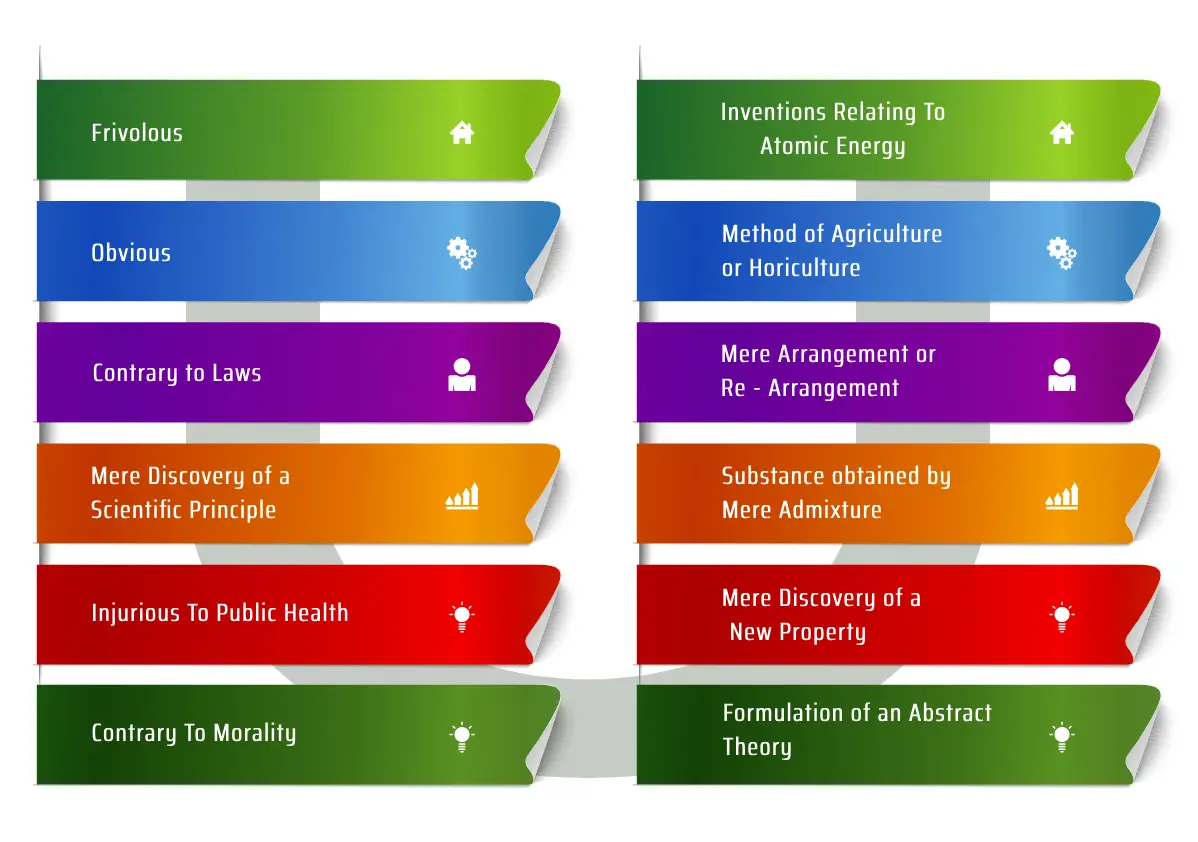
8. Example of Patents